
In order to promote public education and public safety, equal justice for all, a better informed citizenry, the rule of law, world trade and world peace, this legal document is hereby made available on a noncommercial basis, as it is the right of all humans to know and speak the laws that govern them.
ASME B30.14-2004
(Revision of ASME B30.14-1996)
Side Boom Tractors
Safety Standard for Cableways, Cranes, Derricks, Hoists, Hooks, Hacks, and slings
AN AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD



ASME B30.14-2004
(Revision of ASME B30.14-1996)
SAFETY STANDARD FOR CABLEWAYS, CRANES, DERRICKS, HOISTS, HOOKS, JACKS, AND SLINGS
iDate of Issuance: September 20, 2004
The next edition of this Standard is scheduled for publication in 2009. There will be no addenda issued to this edition.
ASME issues written replies to inquiries concerning interpretations of technical aspects of this Standard. Interpretations are published on the ASME Web site under the Committee Pages at http://www.asme.org/codes/ as they are issued, and will also be published within the next edition of the Standard.
ASME is the registered trademark of The American Society of Mechanical Engineers.
This code or standard was developed under procedures accredited as meeting for criteria for American National Standards. The Standard Committee that approved the code or standard was balanced to assure that individuals from competent and concerned interests have had an opportunity to participate. The proposed code or standard was made available for public review and comment that provides an opportunity for additional public input from industry, academia, regulatory agencies, and the public-at-large.
ASME does not “approve,” or “endorse” any item, construction, proprietary device, or activity.
ASME does not take any position with respect to the validity of any patent rights asserted in connection with any items mentioned in this document, and does not undertake to insure anyone utilizing a standard against liability for infringement of any applicable letters patent, nor assume any such liability. Users of a code or standard are expressly advised that determination of the validity of any such patent rights, and risk of infringement of such rights, is entirely their own responsibility.
Participation by federal agency representative(s) or person(s) affiliated with industry is not to be interpreted as government or industry endorsement of this code or standard.
ASME accepts responsibility for only those interpretations of this document issued in accordance with the established ASME procedures and policies, which precludes the issuance of interpretations by individuals.
No part of this document may be reproduced in any form,
in an electronic retrieval system or otherwise,
without the prior written permission of the publisher.
The American Society of Mechanical Engineers
Three Park Avenue, New York, NY 10016-5990
Copyright © 2004 by
THE AMERICAN SOCIETY OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERS
All rights reserved
Printed in U.S.A.
| Foreword | iv | |
| Committee Roster | v | |
| B30 Series Introduction | vii | |
| Summary of Changes | x | |
| Chapter 14-0 | Scope, Definitions, and References | 1 |
| Section 14-0.1 | Scope of B30.14 | 1 |
| Section 14-0.2 | Definitions | 1 |
| Section 14-0.3 | References | 2 |
| Chapter 14-1 | Construction and Characteristics | 4 |
| Section 14-1.1 | Load Ratings | 4 |
| Section 14-1.2 | Boom Hoist and Load Hoist Mechanisms | 4 |
| Section 14-1.3 | Side Boom Tractor Travel | 6 |
| Section 14-1.4 | Controls | 6 |
| Section 14-1.5 | Ropes and Reeving Accessories | 6 |
| Section 14-1.6 | Cabs | 7 |
| Section 14-1.7 | General Requirements | 7 |
| Chapter 14-2 | Inspection, Testing, and Maintenance | 9 |
| Section 14-2.1 | Inspection | 9 |
| Section 14-2.2 | Testing | 10 |
| Section 14-2.3 | Maintenance | 10 |
| Section 14-2.4 | Rope Inspection, Replacement, and Maintenance | 11 |
| Chapter 14-3 | Operation | 13 |
| Section 14-3.1 | Operator Qualifications and Operating Practices | 13 |
| Section 14-3.2 | Handling the Load | 14 |
| Section 14-3.3 | Signals | 14 |
| Section 14-3.4 | Miscellaneous | 15 |
| Figures | ||
| 1 | Track-Type Tractor Side Boom | 2 |
| 2 | Wheel-Type Tractor Side Boom | 2 |
| 3 | Load Rating Chart | 5 |
| 4 | Standard Hand Signals for Controlling Side Boom Tractor Operations | 16 |
| 5 | Danger Zone for Side Boom Tractors and Lifted Loads Operating Near Electrical Transmission Lines | 18 |
| Table | ||
| 1 | Required Clearance for Normal Voltage in Operation Near High Voltage Power Lines and Operation in Transit With No Load and Boom or Mast Lowered | 18 |
This American National Standard, Safety Standard for Cableways, Cranes, Derricks, Hoists, Hooks, Jacks, and Slings, has been developed under the procedures accredited by the American National Standards Institute (formerly the United States of America Standards Institute). This Standard had its beginning in December 1916 when an eight-page Code of Safety Standards for Cranes, prepared by an ASME Committee on the Protection of Industrial Workers, was presented to the annual meeting of the ASME.
Meetings and discussions regarding safety on cranes, derricks, and hoists were held from 1920 to 1925, involving the ASME Safety Code Correlating Committee, the Association of Iron and Steel Electrical Engineers, the American Museum of Safety, the American Engineering Standards Committee (later changed to American Standards Association and subsequently to the USA Standards Institute), Department of Labor—State of New Jersey, Department of Labor and Industry—State of Pennsylvania, and the Locomotive Crane Manufacturers Association. On June 11, 1925, the American Engineering Standards Committee approved the ASME Safety Code Correlating Committee's recommendation and authorized the project with the U.S. Department of the Navy, Bureau of Yards and Docks, and ASME as sponsors.
In March 1926, invitations were issued to 50 organizations to appoint representatives to a Sectional Committee. The call for organization of this Sectional Committee was sent out October 2, 1926, and the committee. organized November 4, 1926, with 57 members representing 29 national organizations. The Safety Code for Cranes, Derricks, and Hoists, ASA B30.2-1943, was created from the eight-page document referred to in the first paragraph. This document was reaffirmed in 1952 and widely accepted as a safety standard.
Due to changes in design, advancement in techniques, and general interest of labor and industry in safety, the Sectional Committee, under the joint sponsorship of ASME and the Naval Facilities Engineering Command, U.S. Department of the Navy, was reorganized as an American National Standards Committee on January 31, 1962, with 39 members representing 27 national organizations.
The format of the previous code was changed so that separate standards (each complete as to construction and installation; inspection, testing, and maintenance; and operation) would cover the different types of equipment included in the scope of B30.
In 1982, the Committee was reorganized as an Accredited Organization Committee, operating under procedures developed by ASME and accredited by the American National Standards Institute.
This Standard presents a coordinated set of rules that may serve as a guide to government and other regulatory bodies and municipal authorities responsible for the guarding and inspection of the equipment falling within its scope. The suggestions leading to accident prevention are given both as mandatory and advisory provisions; compliance with both types may be required by employers of their employees.
In case of practical difficulties, new developments, or unnecessary hardship, the administrative or regulatory authority may grant variances from the literal requirements or permit the use of other devices or methods, but only when it is clearly evident that an equivalent degree of protection is thereby secured. To secure uniform application and interpretation of this Standard, administrative or regulatory authorities are urged to consult the B30 Committee, in accordance with the format described in Section III, before rendering decisions on disputed points.
This volume of the Standard, which was approved by the B30 Committee and by ASME, was approved by ANSI and designated as an American National Standard on January 22, 2004.
Safety codes and standards are intended to enhance public safety. Revisions result from committee consideration of factors such as technological advances, new data, and changing environmental and industry needs. Revisions do not imply that previous editions were inadequate.
iv(The following is the roster of the Committee at the time of approval of this Standard.)
STANDARDS COMMITTEE OFFICERS
P.S. Zorich, Chair
B.D. Closson, Vice Chair
J. D. Wendler, Secretary
STANDARDS COMMITTEE PERSONNEL
N. E. Andrew, Sverdrup Technology, Inc.
W.T. Hargrove, Alternate, ManTech International Corp.
R.E. Bluff, Gantry Constructors, Inc.
R. J. Bolen E.I. DuPont
G.B. Hetherston, Alternate, E.I. DuPont
A.D. Brown, A. D. Brown Co.
L. D. DeMark, International Union of Operating Engineers
S.C. Buck, Alternate, International Union of Operating Engineers
T.A. Christensen Alliance of American Insurers/Liberty Mutual Insurance
M. W. Mills, Alternate, Liberty Mutual Group,
B. D. Closson, NACB Technical Services, Inc.
T. L. Blanton, Alternate, NACB Group, Inc.
J. P. Colletti, John P. Colletti and Associates, Inc.
R.A. Dahlin, Walker Magnetics Group
J. W. Downs, Jr., Alternate Downs Crane and Hoist Co.
D. W. Eckstine, Eckstine and Associates
R. J. Edwards, Schwing America, Inc.
R. H. Fowler U.S. Department of the Air Force
J. L. Franks, Consultant
R. C. Slater, Alternate, McKay International Engineering
J. L. Gordon, FKI Industries, Inc.
R. R. Reisinger, Alternate FKI Industries, Inc.
N. C. Hargreaves Power Crane and Shovel Association /Terex Corp.
E. D. Fidler, Alternate, Terex Corp.
J. J. Headley Crane Institute of America
R. M. Parnell, Alternate, Industrial Training International
C. W. Ireland National Oilwell
A. J. Egging, Alternate, National Oilwell
L.S. Johnson, American Equipment Co.
R. M. Kohner, Landmark Engineering Services
H. I. Shapiro, Alternate, Howard I. Shapiro and Associates Consulting Engineers
H. G. Leidich, Ingersoll-Rand
J. T. Perkins, Alternate Ingersoll-Rand
C. E. Lucas, The Crosby Group
E. K. Marburg, Columbus-McKinnon
M. G. Miller, Alternate, Columbus-McKinnon,
L. D. Means Wire Rope Technical Board/Means Engineering and Consulting
D. M. Sleightholm, Alternate Bridon America Corp.
K. J. Miller Jacobs Engineering Group
G. L. Owens, Granite Construction, Inc.
J.E. Richardson, U.S. Department of the Navy
W. P. Rollins, Manitowoc Crane Group
T. E. Ward-Robichaux, Alternate Lift Solutions, Inc.
J. W. Rowland III, Association of Iron and Steel Engineers/Bethlehem Steel Corp.
E.E. Rudy, U. S. Department of the Army
J. C. Ryan, Boh Bros. Construction Co.
A. Ruud, Alternate, Phillips and Jordan
D. Sayenga Associated Wire Rope Fabricators
D. J. Bishop, Alternate, Bishop Lifting Products, Inc.
G. W. Shields, Caterpillar, Inc.
R. G. Strain, Advanced Automation Technologies, Inc.
A. R. Toth, Morris Material Handling
B. E. Weir, Jr., National Erectors Association/Norris Brothers Co., Inc.
J. Conant, Alternate, Conant Crane Rental Co.
J. D. Wendler, The American Society of Mechanical Engineers
R. C. Wild U. S. Army Corps of Engineers
S. G. Testerman, Alternate U. S. Army Corps of Engineers
D. N. Wolff, National Crane Corp.
A. L. Calta, Alternate, National Crane Corp.
P. S. Zorich, RZP International Ltd.
HONORARY MEMBERS
vJ. M. Klibert, Lift-All Co., Inc.
R. W. Parry, Consultant
B30.14 SUBCOMMITTEE PERSONNEL
viM. G. Miller, Chair, Jacobs Engineering Group
J. Gregory, International Union of Operating Engineers
L. D. Means, Wire Rope Technical Board/Means Engineering and Consulting
G. L. Owens, Granite Construction, Inc.
SAFETY STANDARD FOR CABLEWAYS, CRANES, DERRICKS,
HOISTS, HOOKS, JACKS, AND SLINGS
This Standard is one of a series of safety standards on various subjects that have been formulated under the general auspices of the American National Standards Institute. One purpose of the Standard is to serve as a guide to governmental authorities having jurisdiction over subjects within the scope of the Standard. It is expected, however, that the Standard will find a major application in industry, serving as a guide to manufacturers, purchasers, and users of the equipment.
For the convenience of the user, the Standard has been divided into separate volumes.
| B30.1 | Jacks |
| B30.2 | Overhead and Gantry Cranes (Top Running Bridge, Single or Multiple Girder, Top Running Trolley Hoist) |
| B30.3 | Construction Tower Cranes |
| B30.4 | Portal, Tower, and Pedestal Cranes |
| B30.5 | Mobile and Locomotive Cranes |
| B30.6 | Derricks |
| B30.7 | Base Mounted Drum Hoists |
| B30.8 | Floating Cranes and Floating Derricks |
| B30.9 | Slings |
| B30.10 | Hooks |
| B30.11 | Monorails and Underhung Cranes |
| B30.12 | Handling Loads Suspended From Rotorcraft |
| B30.13 | Storage/Retrieval (S/R) Machines and Associated Equipment |
| B30.14 | Side Boom Tractors |
| B30.15 | Mobile Hydraulic Cranes Note: B30.15-1973 has been withdrawn. The revision of B30.15 is included in the latest edition of B30.5. |
| B30.16 | Overhead Hoists (Underhung) |
| B30.17 | Overhead and Gantry Cranes (Top Running) |
| B30.18 | Stacker Cranes (Top or Under Running Bridge, Multiple Girder With Top or Under Running Trolley Hoist) |
| B30.19 | Cableways |
| B30.20 | Below-the-Hook Lifting Devices |
| B30.21 | Manually Lever Operated Hoists |
| B30.22 | Articulating Boom Cranes |
| B30.23 | Personnel Lifting Systems |
| B30.24 | Container Cranes1 |
| B30.25 | Scrap and Material Handlers |
| B30.26 | Rigging Hardware1 |
| B30.27 | Material Placement Systems1 |
| B30.28 | Balance-Lifting Units1 |
| 1 B30.24, B30.26, B30.27, and B30.28 are in the developmental stage. | |
If these standards are adopted for governmental use, the references to other national codes and standards in the specific volumes may be changed to refer to the corresponding regulations of the governmental authorities.
The use of cableways, cranes, derricks, hoists, hooks, jacks, and slings is subject to certain hazards that cannot be met by mechanical means but only by the exercise of intelligence, care, and common sense. It is therefore essential to have personnel involved in the use and operation of equipment who are competent, careful, physically and mentally qualified, and trained in the safe operation of the equipment and the handling of the loads. Serious hazards are overloading, dropping or slipping of the load caused by improper hitching or slinging, obstructing the free passage of the load, and using equipment for a purpose for which it was not intended or designed.
The Standards Committee fully realizes the importance of proper design factors, minimum or maximum sizes, and other limiting dimensions of wire rope or chain and their fastenings, sheaves, sprockets, drums, and similar equipment covered by the Standard, all of which are closely connected with safety. Sizes, strengths, and similar criteria depend on many different factors, often varying with the installation and uses. These factors depend on the condition of the equipment or material; the loads; the acceleration or speed of the ropes, chains, sheaves, sprockets, or drums; the type of attachments; the number, size, and arrangement of sheaves or other parts; environmental conditions causing corrosion or wear; and many variables that must be considered in each individual case. The rules given in the Standard must be interpreted accordingly, and judgment must be used in determining their application.
The Standards Committee will be glad to receive criticisms of this Standard's requirements and suggestions
viifor its improvement, especially those based on actual experience in application of the rules.
Suggestions for changes to the Standard should be submitted to the Secretary of the B30 Committee, ASME, Three Park Avenue, New York, NY 10016-5990, and should be in accordance with the following format:
(a) Cite the specific paragraph designation of the pertinent volume.
(b) Indicate the suggested change (addition, deletion, revision, etc.).
(c) Briefly state the reason and/or evidence for the suggested change.
(d) Submit suggested changes to more than one paragraph in the order that the paragraphs appear in the volume.
The B30 Committee will consider each suggested change in a timely manner in accordance with its procedures.
This Standard applies to the construction, installation, operation, inspection, and maintenance of jacks, power operated cranes, monorails, and crane runways; power operated and manually operated derricks and hoists; lifting devices, hooks, and slings, and cableways.
This Standard does not apply to track and automotive jacks, railway or automobile wrecking cranes, shipboard cranes, shipboard cargo-handling equipment, well-drilling derricks, skip hoists, mine hoists, truck body hoists, car or barge pullers, conveyors, excavating equipment, or equipment falling with in the scope of the following Committees: A10, A17, A90, A92, A120, B20, B56, and B77.
This Standard is designed to
(a) guard against and minimize injury to workers, and otherwise provide for the protection of life, limb, and property by prescribing safety requirements
(b) provide direction to owners, employers, supervisors, and others concerned with, or responsible for, its application
(c) guide governments and other regulatory bodies in the development, promulgation, and enforcement of appropriate safety directives
Upon request, the B30 Committee will render an interpretation of any requirements of the Standard. Interpretations can only be rendered in response to a written request sent to the Secretary of the B30 Committee, ASME, Three Park Avenue, New York, NY 10016-5990.
The request for interpretation should be clear and unambiguous. It is further recommended that the inquirer submit his request utilizing the following format.
| Subject: | Cite the applicable paragraph number(s) and provide a concise description. |
| Edition: | Cite the applicable edition of the pertinent volume for which the interpretation is being requested. |
| Question: | Phrase the question as a request for an interpretation of a specific requirement suitable for general understanding and use, not as a request for approval of a proprietary design or situation. The inquirer may also include any plans or drawings that are necessary to explain the question; however, they should not contain any proprietary names or information. |
Requests that are not in this format will be rewritten in this format by the Committee prior to being answered, which could change the intent of the original request.
ASME procedures provide for reconsideration of any interpretation when or if additional information that might affect an interpretation is available. Further, persons aggrieved by an interpretation may appeal to the cognizant ASME Committee or Subcommittee. ASME does not “approve” “certify,” “rate,”” or “endorse” any item, construction, proprietary device, or activity.
(a) Effective Date. The effective date of this volume for the purpose of defining new and existing installations shall be 1 year after its date of issuance.
(b) New Installations. Construction, installation, inspection, testing, maintenance, and operation of equipment manufactured and facilities constructed after the effective date of this volume shall conform to the mandatory requirements of this volume.
(c) Existing Installations. Inspection, testing, maintenance, and operation of equipment manufactured and facilities constructed prior to the effective date of this volume shall be done, as applicable, in accordance with the requirements of this volume.
It is not the intent of this volume to require retrofitting of existing equipment. However, when an item is being modified, its performance requirement shall be reviewed
viiirelative to the current volume. If the performance differs substantially, the need to meet the current requirement shall be evaluated by a qualified person selected by the owner (user). Recommended changes shall be made by the owner (user) within 1 year.
Mandatory rules of this volume are characterized by use of the word shall. If a provision is of an advisory nature, it is indicated by use of the word should and is a recommendation to be considered, the advisability of which depends on the facts in each situation.
This Standard contains SI (metric) units as well as U.S. Customary units. The values stated in U.S Customary units are to be regarded as the standard. The SI units are a direct (soft) conversion from the customary units.
ixFollowing approval by the ASME B30 Committee and ASME, and after public review, ASME B30.14-2004 was approved by the American National Standards Institute on January 22, 2004.
ASME B30.14-2004 includes editorial changes, revisions, and corrections introduced in ASME B30.14a-1997, B30.14b-1999, B30.14c-2001, as well as the following changes identified by a margin note, (04).
| Page | Location | Change |
| vii, ix | B30 Series Introduction | General and Section VI revised |
SIDE BOOM TRACTORS
Volume B30.14 includes provisions that apply to the construction, installation, operation, inspection, testing, and maintenance of side boom tractors powered by an internal combustion engine used for pipe laying or lifting operations, utilizing a lifting boom, drum, wire rope, and/or hydraulic cylinders.
The requirements for a side boom tractor that is used for other than lifting operations such as when converted for excavating work, and a side boom tractor with a rated load of one ton or less, are not included in this Volume.
accessory: a secondary part or assembly of parts that contributes to the effectiveness of a machine.
administrative or regulatory authority: governmental agency or the employer in the absence of governmental jurisdiction.
appointed: assigned specific responsibilities by the employer or the employer's representative.
approved: accepted as satisfactory by a duly constituted administrative or regulatory authority.
authorized: approved by a duly constituted administrative or regulatory authority.
axle: the shaft or spindle with which or about which a wheel rotates. On side boom tractors and wheel-type tractors it refers to an assembly that includes the shaft, housing, and gearing from the shaft to the wheel, sprocket, or equivalent device.
boom hoist: a hoist drum and rope reeving system used to raise and lower the boom. The rope system may be all live reeving or a combination of live reeving and pendants. The boom may also be raised and lowered by a hydraulic cylinder(s).
boom stop: an automatic device used to limit the angle of the boom at the highest position.
brake: a device used for retarding or stopping motion by friction or power means.
clutch: a friction, electromagnetic, hydraulic, pneumatic, or positive mechanical device for engagement or disengagement of power.
counterweight: weight used to supplement the weight of the machine in providing stability for lifting loads.
designated person: a person selected or assigned by the employer or the employer's representative as being competent to perform specific duties.
drum: the cylindrical members around which ropes are wound.
dynamic loading: loads introduced into the machine or its components by forces in motion.
load: the external load, in pounds (kilograms) applied to the side boom tractor, including the weight of load-attaching equipment such as load blocks, shackles, and slings.
load, rated: side boom tractor ratings in pounds (kilograms) established by the manufacturer in accordance with para. 14-1.1.
load block, lower: the assembly of hook or shackle, swivel, sheaves, pins, and frame suspended by the hoisting ropes.
load block, upper: the assembly of hook or shackle, swivel, sheaves, pins, and frame suspended from the boom point.
load capacity, maximum: the capacity for which the tractor is designed (Refer to SAE J743.).
load hoist: a hoist drum and rope reeving system used for lifting and lowering loads.
load overhang, track-type tractor: the horizontal distance from the center of the load hook to the outer edge of the outer track rail on the boom side (Refer to SAE J743.).
load overhang, wheel-type tractor: the horizontal distance from the center of the load hook measured perpendicular
1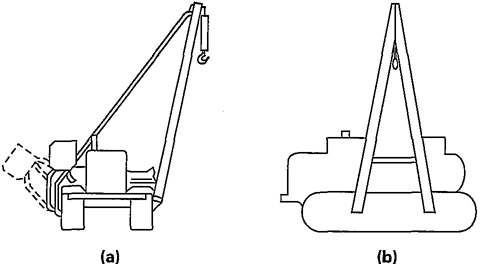
Fig. 1 Track-Type Tractor Side Boom
to the center line of the tires on the boom side (Refer to SAE J743.).
qualified person: a person who, by possession of a recognized degree in an applicable field, or certificate of professional standing, or who, by extensive knowledge, training, and experience, has successfully demonstrated the ability to solve or resolve problems relating to the subject matter and work.
reeving: a rope system in which the rope travels around drums and sheaves.
rope: refers to wire rope unless otherwise specified.
service, heavy: service that involves operation within the rated load limit that exceeds normal service.
service, normal: distributed service that involves operation with randomly distributed loads within the rated load limit, or uniform loads less than 65% of rated load for not more than 25% of the time.
service, severe: service that involves normal or heavy service with abnormal operating conditions.
shall: if a provision is of a mandatory nature it is indicated by the use of the word shall.
should: if a provision is of an advisory nature, it is indicated by the use of the word should and is a recommendation to be considered, the advisability of which depends on the facts in each situation.
side boom tractor: a track-type (Fig. 1) or wheel-type tractor (Fig. 2) having a boom mounted on the side of the tractor, used for lifting, lowering, or transporting a load suspended on the load hook. The boom or hook can be lifted or lowered in a vertical direction only.
side loading: a load applied at an angle to the vertical plane of the boom.
stabilizers: extendable or fixed metal arms attached to the mounting base, that rest on supports at the outer ends.
standing rope (guy): a supporting rope that maintains a constant distance between the points of attachment to the two components connected by the rope.
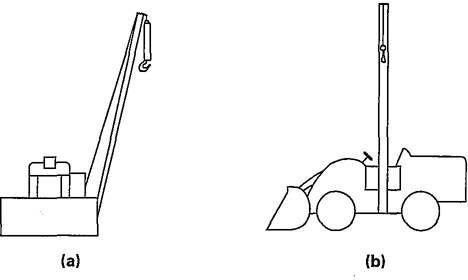
Fig. 2 Wheel-Type Tractor Side Boom
structural competence: the ability of the machine and its components to withstand the stresses imposed by applied loads.
tackle: an assembly of ropes and sheaves arranged for lifting and pulling.
tipping condition, track-type tractor: the load on the hook at the given load overhang distance that will cause the track roller of the track opposite the boom side to lift ¼ in. (6.4 mm) from the rail.
tipping condition, wheel-type tractor: the load on the hook, in pounds (kilograms), at the given load overhang distance that will cause the wheel on the side opposite the boom to leave the ground  in. (1.6 mm).
in. (1.6 mm).
transit: the moving or transporting of a side boom tractor from one location to another.
travel: the function of the machine moving from one location to another, on a job site.
travel mechanism: the machinery involved in providing travel.
wheelbase: distance between centers of front and rear axles. For a multiple-axle assembly, the axle center for wheelbase measurement is taken as the midpoint of the assembly.
The following is a list of publications referenced in this Standard.
ANSI Z26.1-1990, Safety Code for Glazing Materials for Glazing Motor Vehicle Operating on Land Highways
Publisher: American National Standards Institute, 25 West 43rd Street, New York, NY 10036
ASME B30.5-2000, Mobile and Locomotive Cranes1
ASME B30.9-1990, Slings1
ASME B30.10-1993, Hooks1
1 Copies may also be obtained from the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 West 43rd Street, New York, NY 10036.
2Publisher: The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME International), Three Park Avenue, New York, NY 10016-5990; ASME Order Department: 22 Law Drive, Box 2300, Fairfield, NJ 07007-2300
AWS D14.3-93, Specification for Welding Earthmoving and Construction Equipment1
Publisher: American Welding Society, 550 NW Le Jeune Road, Miami, FL 33126
SAE J185-1988, Access Systems for Off-Road Machines1
SAE J743-1992, Pipe Layers and Side Booms—Tractor Mounted1
Publisher: Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), 400 Commonwealth Drive, Warrendale, PA 15096-0001
314-1.1.1 Load Ratings—Where Stability Governs Lifting Performance
Load ratings at the minimum load overhang may be based on structural competence rather than stability. Refer to para. 14-1.1.2.
(a) The margin of stability for determination of load ratings, with booms of stipulated lengths at stipulated load overhang for the various type of tractor mountings, is established by taking a percentage of the loads that will produce a condition of tipping. The load ratings shall not exceed the following percentages for side boom tractors, with the indicated types of mounting under conditions stipulated in paras. 14-1.1.1(b) and (c).
| Type of Machine | Rated Load (Percent of Maximum Load Capacity Based on SAE J743 Test Procedure) |
|---|---|
| Track-type tractor | 85% |
| Wheel-type tractor | 65% |
(b) The following stipulations shall govern the application of the values in para. 14-1.1.1(a) for side boom tractors:
(1) Lift capacity from which ratings are determined shall be applied under static conditions only, i.e., without dynamic effect of lifting or lowering.
(2) The weight of all auxiliary handling devices such as hoist blocks, hooks, and slings shall be considered a part of the load rating.
(c) Stipulations governing the application of the values in para. 14-1.1.1(a) for track-type side boom tractors and wheel-type side boom tractors shall be in accordance with tractor side boom testing procedure SAE J743.
(d) The effectiveness of these preceding stability factors will be influenced by such additional factors as freely suspended loads, wind or ground conditions, condition and inflation of rubber tires, boom lengths, operating speeds for existing conditions, and in general, careful and competent operation. All of these shall be taken into account by the user.
14-1.1.2 Load Ratings—Where Structural Competence Governs Lifting Performance
Load ratings are governed by the stability of the side boom tractor, i.e., the load required to tip the side boom tractor at a given load overhang. However, in some areas of the operating range, the ratings may be governed by factors other than stability, such as the conditions described below.
(a) Load ratings at the minimum load overhang may be based on structural competence of the machine rather than stability.
(b) Load ratings at some load overhangs are governed by structural competence, and side boom tractor stability cannot be used as a basis of load rating. Manufacturer's recommendations shall not be exceeded.
14-1.1.3 Load Rating Chart
A load rating chart, based on Fig. 3, with legible letters and figures shall be provided with each side boom tractor and affixed in a location visible to the operator while seated at the control station. The data and information to be provided on these charts shall include, but not necessarily be limited to the following:
(a) a range of manufacturer's recommended side boom tractor rated loads at stated operating load overhang for permissible boom lengths and for all configurations and modifications, but not limited to stabilizers or additional counterweight.
(b) the basis of ratings as found in para. 14-1.1.1, including the identification of ratings if based on structural limitations. Where ratings are limited by structural competence or rope design factors as shown in para. 14-1.5.1(a), such ratings shall be shown and emphasized on the rating charts and by listing the special provisions of para. 14-3.2.1(c).
(c) recommended parts of hoist reeving, size, and type of rope for various hook loads shall be shown on the rating chart and in the operating manual.
(d) a rating chart shall be prepared by a qualified person for all nonstandard modifications including boom length.
14-1.2.1 Boom Hoist Mechanism
When using recommended boom hoist reeving or hydraulic cylinder system with maximum load capacity suspended, the boom hoist mechanism shall be capable of raising or lowering the boom, stopping boom motion, and holding it stationary without attention from the operator.
4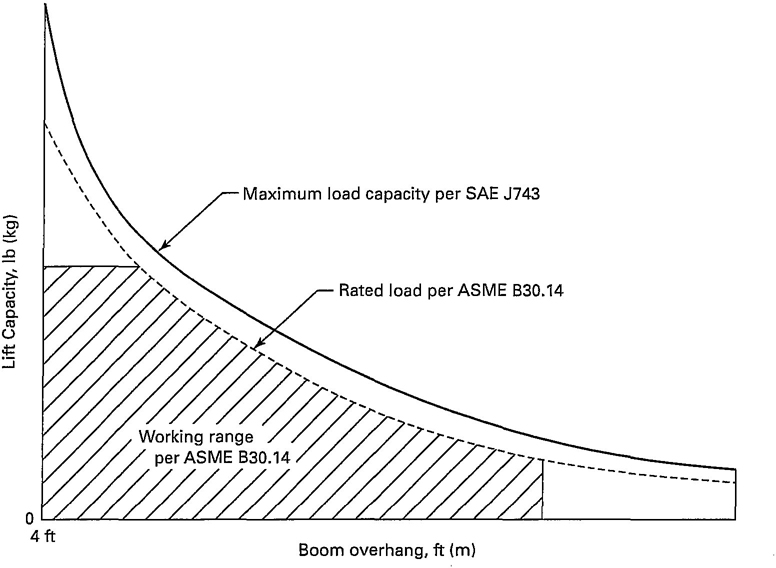
Fig. 3 Load Rating Chart
(a) The boom hoist mechanism shall be provided with a clutch or power engaging device permitting immediate starting or stopping of the boom motion. The boom hoist mechanism shall also be provided with a self-setting brake or hydraulic system, capable of supporting the maximum load capacity.
(b) Brakes and clutches shall be provided with adjustments where necessary to compensate for wear and to maintain adequate force in springs where used.
(c) The boom hoist mechanism shall be provided with an auxiliary ratchet and pawl or other positive locking device to prevent inadvertent lowering of the boom.
(d) The boom hoist drum shall have sufficient rope capacity to operate the boom at all positions from horizontal to the highest angle utilizing recommended reeving and rope diameter.
(1) Not less than two full wraps of rope shall remain on the drum with boom point lowered to the level of the tractor supporting surface.
(2) The rope end shall be anchored by a clamp attached to the drum or by a wedge socket arrangement approved by the side boom or rope manufacturer. The rope clamp shall be tightened evenly to the manufacturer's recommended torque.
(e) The drum diameter shall provide a first layer rope pitch diameter of not less than 10 times the nominal diameter of the rope used.
14-1.2.2 Load Hoist Mechanism
(a) Load Hoist Drums. The load hoist drum assemblies shall have power and operational characteristics to perform all load lifting and lowering functions required in side boom tractor service when operated under recommended conditions.
(1) Where brakes and clutches are used to control the motion of the load hoist drums, they shall be of size and thermal capacity to control maximum load capacity with minimum recommended reeving. (When maximum load capacity is being lowered with near maximum boom length on operations involving long lowering distances, power controlled lowering usually is necessary to reduce demand on the load brake.)
(2) Load hoist drums shall have rope capacity with recommended rope size and reeving to perform side boom tractor service as defined in para. 14-0.1, within the range of boom lengths, operating overhang, and vertical lifts stipulated by the manufacturer.
(a) Not less than two full wraps of rope shall remain on the drum when the hook is in its extreme low working position.
(b) The rope end shall be anchored by a clamp attached to the drum or by a wedge socket arrangement approved by the side boom or rope manufacturer. The rope clamp shall be tightened evenly to the manufacturer's recommended torque.
5(c) Drums shall be provided with a means to prevent rope from jumping off the drum.
(3) Diameter of the load hoist drums shall provide a first layer rope pitch diameter of no less than 10 times the nominal diameter for the rope used.
(4) Positive means, controllable from the operator's station, shall be provided to prevent the drum from rotating in the lowering direction and be capable of holding the maximum load capacity without further attention from the operator.
(b) Load Hoist Brakes. When power operated brakes, having no continuous mechanical linkage between the actuating and braking means, are used for controlling loads, an automatic means shall be provided to prevent the load from falling in the event of loss of brake actuating power.
(c) Power-Controlled Lowering. A power-controlled lowering device shall be capable of handling maximum load capacity and speeds as specified by the manufacturer. Such a device is recommended to provide precision lowering and to reduce demand on the load brake.
14-1.2.3 Adjustments
Brakes and clutches shall be provided with adjustments where necessary to compensate for lining wear.
14-1.3.1 Travel Controls
The controls for the travel function shall be located at the operator's station.
14-1.3.2 Travel Brakes and Locks
Brakes or other locking means shall be provided to hold the machine stationary within the limits of traction, during working cycles on level grade or while the machine is standing on maximum grade recommended for travel. Such brakes or locks shall be arranged to remain in engagement in event of loss of operating pressure.
14-1.4.1 Side Boom Operation
All controls used during normal side boom tractor operations shall be located within reach of the operator while seated at the operator's station, and controls shall be labeled as to function.
14-1.4.2 Control Forces and Movement
For hoisting controls, the following shall be provided:
(a) forces not greater than 35 lb (155 N) on hand levers
(b) travel distance on hand levers not greater than 15 in. (380 mm) from neutral position on two-way levers and not greater than 24 in. (610 mm) on one-way levers
14-1.4.3 Power Plant Controls
Controls for operating the power plant shall be within reach of the operator and shall include the following means:
(a) start and stop
(b) control speed
(c) emergency stop
(d) shifting selective transmission
14-1.4.4 Engine Clutch
All side boom tractors having mechanical draw works shall be provided with a means for disengaging power to the draw works. The control shall be within reach from the operator's station.
14-1.5.1 Rope Design Factors
(a) When supporting rated loads (including load suspensions):
(1) the design factor for live or running ropes that wind on drums or pass over sheaves shall be not less than 4.0
(2) the design factor for boom pendants or standing ropes shall be not less than 3.5
(b) When supporting the maximum load capacity (including load suspensions) [refer to para. 14-1.1.3(b)], the special provisions of para. 14-3.2.1(c) shall be followed.
(c) The design factors specified above shall be determined on the basis of the manufacturer's ratings, with approved reeving, published minimum breaking strength of new ropes, and with load and boom stationary.
NOTE: Minimum breaking strength formerly referred to as nominal breaking strength.
14-1.5.2 Ropes
(a) The hoist rope shall be of a construction recommended for side boom tractor service. Rotation resistant rope shall not be used.
(b) Socketing shall be done in the manner specified by the manufacturer of the wire rope or fitting.
(c) If a load is supported by more than one part of rope, the tension in the parts shall be equalized.
(d) Wherever exposed to temperatures at which fiber cores would be damaged, rope having an independent wire-rope or wire-stand core, or other temperature-damage resistant core shall be used.
14-1.5.3 Reeving Accessories
(a) Eye splices shall be made in accordance with manufacturer's recommendations and rope thimbles shall be used in the eye splices.
6(b) Wire rope clips shall be drop-forged steel of the single saddle (U-bolt) or double saddle type clip. Malleable cast iron clips shall not be used. For spacing, number of clips, and torque values, refer to the clip manufacturer's recommendation. Wire rope clips attached with U-bolts shall have the U-bolt over the dead end of the rope and the live rope resting in the clip saddle. Clips shall be tightened evenly to the recommended torque. After the initial load is applied to the rope, the clip nuts shall be retightened to the recommended torque to compensate for any decrease in rope diameter caused by the load. Rope clip nuts should be retightened periodically to compensate for any further decrease in rope diameter during usage.
(c) Swaged, compressed, or wedge socket fittings shall be applied as recommended by the rope, side boom tractor, or fitting manufacturer.
14-1.5.4 Sheaves
(a) Sheave grooves shall be free from surface defects that could cause rope damage. The cross-sectional radius at the bottom of the groove should be such as to form a close-fitting saddle for the size of rope used. The sides of the groove shall be tapered outward and rounded at the rim to facilitate entrance of the rope into the groove. Flange rims shall run true about the axis of rotation.
(b) Sheaves carrying ropes that can be momentarily unloaded shall be provided with close-fittings guards or other suitable devices to guide the rope back into the groove when the load is applied again.
(c) Sheaves in the lower load block shall be equipped with close-fitting guards that will prevent ropes from becoming fouled when the block is lying on the ground with ropes loose.
(d) Means shall be provided to prevent chafing of the ropes.
(e) All sheave bearings shall be provided with means for lubrication. Permanently lubricated bearings are acceptable.
14-1.5.5 Sheave Sizes
(a) Boom hoisting sheaves shall have pitch diameters of not less than 10 times the nominal diameter of the rope used.
(b) Load hoisting sheaves shall have pitch diameters of not less than 10 times the nominal diameter of the rope used.
(c) Load block sheaves shall have pitch diameters of not less than 10 times the nominal diameter of the rope used.
14-1.6.1 Construction
(a) Cabs, if provided, shall be constructed to enclose the operator's station to provide protection from the weather, and shall include all boom and tractor controls.
(b) Windows or openings shall be provided in the cab or operator's compartment on all four sides of the cab for maximum visibility.
(c) All cab glazing shall be safety glazing material as defined in ANSI Z26.1.
(d) Visibility on the boom side of the cab shall be such that the uppermost point of the boom is visible at all times.
(e) If a congested operator's station precludes a cab having doors on both sides, a second exit shall be provided.
(f) All cab doors, whether of sliding or swinging type, shall be restrained from inadvertent opening or closing while traveling or operating the machine. The door adjacent to the operator, if the swinging type, should open outward and, if the sliding type, should slide rearward to open.
(g) A clear passageway shall be provided from the operator's station to an exit door on the operator's side.
14-1.6.2 Platforms
(a) Principal walking surfaces shall be of a skid resistant type.
(b) Outside platforms, if furnished, shall be provided with guardrails in accordance with SAE J185. Where platforms are too narrow to use guardrails, handholds shall be provided at points above the platform.
14-1.6.3 Access
On all crawler and wheel-mounted side boom tractors, handholds and steps shall be provided, as needed, to facilitate entrance to and exit from the operator's cab.
14-1.6.4 Cab Roof
Where necessary for rigging or service requirements, a ladder or steps shall be provided to give access to a cab roof. The ladder, steps, and weight-supporting capability of the cab roof shall conform to the requirements of SAE J185.
14-1.6.5 Noise Exposure
The noise level at the operator's station shall be a consideration in the manufacture of new tractors.
14-1.7.1 Booms
(a) Boom stops shall be provided.
(b) Automatic means shall be provided to stop boom motion when the maximum permissible boom angle is reached.
(c) Booms shall meet the performance requirements of side boom tests in SAE J743.
714-1.7.2 Exhaust Gases
Engine exhaust gases shall be piped to the outside of the cab and discharged in a direction away from the operator. All exhaust pipes shall be guarded or insulated in areas where contact by personnel is probable in the performance of normal duties.
14-1.7.3 Stabilizers (Wheel-Type Side Boom Tractors)
(a) Means shall be provided to hold all stabilizers in the retracted position while traveling and in the extended position when blocked for lifting. When stabilizers are used, all stabilizers shall be extended.
(b) Power-actuated jacks, where used, shall be provided with means to prevent loss of support under load.
(c) Each stabilizer shall be visible from its actuating location.
(d) Means shall be provided for fastening stabilizer floats to stabilizers when in use.
14-1.7.4 Welded Construction
All welding procedures and welding operator qualifications to be used on load sustaining members shall be in accordance with AWS D14.3. Where special steels or other materials are used, the manufacturer shall provide welding procedures.
14-1.7.5 Guards for Moving Parts
(a) Exposed moving parts such as gears, set screws, projecting keys, chain sprockets, and reciprocating parts that constitute a hazard shall be guarded.
(b) Guards shall be fastened.
(c) Each guard shall be capable of supporting without permanent distortion the weight of a 200 lb (90 kg) person unless the guard is located where it is not probable that a person will step on it.
14-1.7.6 Clutch and Brake Protection
Friction brakes and clutches shall be provided with rain guards.
14-1.7.7 Lubricating Points
Lubricating points should be accessible without the necessity of removing guards.
14-1.7.8 Miscellaneous Equipment
tool box: a receptacle should be secured permanently to the side boom tractor for storing tools and lubricating equipment.
814-2.1.1 Inspection Classification
(a) Initial Inspection. Prior to initial use, all new, reinstalled, altered, or modified side boom tractors shall be inspected by a designated person to verify compliance with the provisions of this volume.
(b) Inspection procedure for side boom tractors in regular service is divided into two general classifications based upon the intervals at which inspection should be performed. The intervals in turn are dependent upon the nature of the critical components of the side boom tractor and the degree of their exposure to wear, deterioration, or malfunction. The two general classifications are herein designated as frequent and periodic, with respective intervals between inspection as defined below.
(1) Frequent Inspection. Visual examination by the operator or other designated personnel with records not required.
(a) normal service—monthly
(b) heavy service—weekly to monthly
(c) severe service—daily to weekly
(d) special or infrequent service is recommended by a qualified individual before and after each occurrence
(2) Periodic Inspection. Visual inspection by an appointed person making records of apparent external conditions to provide the basis for a continuing evaluation.
(a) normal service—annually
(b) heavy service—semi-annually
(c) severe service—quarterly
(d) special or infrequent service as authorized by a qualified person before the first such occurrence and as directed by the qualified person for any subsequent occurrences
14-2.1.2 Frequent Inspection
(a) Frequent inspections shall be performed at intervals defined in para. 14-2.1.1(b)(1) and shall include observations during operation.
(b) A designated person shall determine whether conditions found during the inspection constitute a hazard and whether a more detailed inspection is required.
(c) The following items shall be inspected:
(1) operating mechanisms for proper operation, proper adjustment—daily, when in use
(2) safety devices for proper operations
(3) lines, tanks, valves, pumps, and other parts of air or hydraulic systems for leaks—daily, when in use
(4) hooks in accordance with ASME B30.10, para. 10.1.2.1.2
(5) hook latches, if used, for proper operation—daily, when in use
(6) hoist rope in accordance with para, 14.2.4.1(a)
(7) electrical apparatus for proper operation, and evidence of excessive deterioration, dirt, and moisture accumulation.
(8) standing ropes (guys), including end connections, for wear [as defined in para. 14.2.4.2(b)], broken wires, stretch, kinking, or twisting
(9) rope reeving for compliance with side boom manufacturer's recommendations
14-2.1.3 Periodic Inspection
Complete inspections of the side boom tractor shall be performed at intervals, as defined in para. 14-2.1.1(b)(2). Any deficiencies, such as listed, shall be examined and determination made as to whether they constitute a hazard. These inspections shall include the requirements of para. 14-2.1.2 and, items such as the following:
(a) deformed, cracked, or corroded members
(b) loose bolts or rivets
(c) cracked or worn sheaves and drums
(d) worn, cracked, or distorted parts such as pins, bearings, shafts, gears, rollers, and locking and clamping devices
(e) excessive wear on brake system parts, linings, pawls, and ratchets
(f) gasoline, diesel, electric or other power plants for improper performance or noncompliance with other applicable standards
(g) excessive were of chain drive sprockets and excessive chain stretch
(h) travel steering, braking, and locking devices, for malfunction
(i) excessively worn or damaged tires or wheels
14-2.1.4 Side Boom Tractors Not in Regular Use
(a) A side boom tractor that has been idle for a period of one month or more, but less than one year, shall be given an inspection conforming with the requirements or paras. 14-2.1.2 and 14-2.4.1(c) before being placed in service.
9(b) Standby side booms shall be inspected at least semiannually in accordance with the requirements of paras. 14-2.1.2 and 14-2.4.1(c), and if exposed to adverse environments, should be inspected more frequently.
14-2.1.5 Inspection Records
Dated inspection reports and records shall be made monthly on critical items in use such as brakes, hooks, and ropes. Dated records should be kept where readily available to appointed personnel.
14-2.2.1 Operational Testing
(a) Prior to initial use, all new, altered, or modified side boom tractors shall bet tested by a designated person to verify compliance with this volume including the following functions:
(1) lifting and lowering
(2) boom up and down
(3) limit devices, such as boom stops should be tested by raising the boom slowly until the boom stop prevents further raising of the boom
(b) Prior to initial use, a repaired side boom tractor shall be tested. Testing may be limited to the function(s) affected by the repair.
14-2.2.2 Rated Load Test
(a) Prior to initial use:
(1) All new side boom tractors shall be bested and all altered or modified side boom tractors shall be tested and inspected by or under the direction of a qualified person. A written test report shall be prepared by the qualified person and placed on file. Test loads shall not exceed 110% of the manufacturer's maximum load capacity and shall not exceed tipping load at any selected working load overhang.
(2) The need for testing of repaired side boom tractors shall be determined by a qualified person. When a rated load test is required, testing shall be in accordance with para. 14-2.2.2(a)(1).
(b) Rated load test shall consist of the following operations as a minimum requirements:
(1) hoist the test load to assure that the load is supported by the side boom tractor and held by the hoist brake(s)
(2) boom the side boom tractor up and down within the working load overhang
(3) travel with the test load a distance sufficient to prove the ability of the side boom to support the test load
(c) No side boom tractor shall be rerated in excess of the original load ratings unless such rating changes are approved by the side boom tractor manufacturer.
14-2.3.1 Preventative Maintenance
(a) A preventative maintenance program should be established and be based on the side boom tractor manufacturer's or a qualified person's recommendation. Dated records should be kept where readily available to appointed personnel.
(b) Replacement parts shall be at least equal to the original manufacturer's specifications.
14-2.3.2 Maintenance Procedure
(a) Before adjustments and repairs are started on a side boom tractor, the following precautions shall be taken as applicable:
(1) side boom tractor placed where it will cause the least interface with other equipment or operations in the area
(2) all controls at the manufacturer's recommended position
(3) starting means rendered inoperative, except when required for repairs
(4) warning or out of order signs placed on the side boom tractor
(5) power plant stopped of disconnected at take-off
(6) boom lowered to the ground, if possible, or otherwise secured against dropping
(7) lower load block lowered to the ground, if possible, or otherwise secured against dropping
(b) After adjustments and repairs have been made, the side boom tractor shall not be returned to service until all guards have been reinstalled, safety devices reactivated, and maintenance equipment removed.
14-2.3.3 Adjustments and Repairs
(a) Any hazardous conditions, disclosed by the inspection requirements of para. 14-2.1, shall be corrected before normal operation of the side boom tractor is resumed. Adjustments and repairs shall be done only by designated personnel.
(b) Adjustments shall be maintained to assure correct functioning of components. The following are examples:
(1) all functional operating mechanisms
(2) limit devices
(3) control systems
(4) brakes
(c) Repairs or replacements shall be made as needed. The following are examples:
(1) side boom tractor hooks showing defects described in para. 14-2.1.2(c)(4) and ASME B30.10 shall be taken out of service. Repairs by welding or reshaping are not recommended. Repairs shall be done under supervision by a qualified person and the hook shall be tested to the load requirement of para. 14-2.2.1 before further use.
10(2) load attachment chains and rope slings having any of the conditions described in para. 14-2.1.2(c)(8).
(3) all critical parts that are cracked, broken, bent, or excessively worn.
(d) If repairs of load sustaining members are made by welding, identification of materials shall be made and appropriate welding procedure shall be followed.
14-2.3.4 Lubrication
(a) A lubrication chart should be available on the side boom tractor.
(b) All moving parts of the side boom tractor for which lubrications is specified, including rope and chain, should be regularly lubricated. Lubricating systems should be checked for proper delivery of lubricant. Care should be taken to follow recommendations of the manufacturer as to points and frequency of lubrication, maintenance of lubricant levels, and types of lubricant to be used. It the manufacturer cannot supply this information a qualified person should be consulted.
(c) Machinery shall be stationary while lubricants are being applied and protection provided as called for in paras. 14-2.3.2 (a)(2) through 14-2.3.2(a)(5), unless equipped for automatic lubrication.
14-2.4.1 Rope Inspection
(a) All running ropes in continuous service shall be visually inspected once each working day. An inspection of all ropes shall be made at least monthly and a dated report of rope condition kept on file where available to appointed personnel. All inspections shall be performed by an appointed person. Sections of rope that are normally hidden during visual and maintenance inspection, such as parts passing over sheaves, should be given close inspection as these are points most likely to fail. Any deterioration resulting in appreciable loss of original strength, such as described below, shall be noted and determination made as to whether further use of the rope would constitute a hazard:
(1) reduction of rope diameter, below nominal diameter due to loss of core support, internal or external corrosion, or wear of outside wires.
(2) a number of broken outside wires and the degree of distribution or concentration of such broken wires.
(3) worn outside wires
(4) corroded or broken wires at end connections
(5) corroded, cracked, bent, worn, or improperly applied end connections
(6) kinking, crushing, cutting, or unstranding
(b) Heavy wear or broken wires may occur in sections in contact with equalizer sheaves of other sheaves where rope travel is limited, or with saddles. Care shall be taken to inspect ropes at these locations.
(c) All rope that has been idle for a period of a month or more due to shutdown or storage of a side boom tractor on which it is installed shall be given a thorough inspection before it is placed in service. This inspection shall be for all types of deterioration and shall be performed by an appointed or authorized person whose approval shall be required for further use of the rope. A dated report of the rope condition shall be filed.
(d) Care shall be taken in the inspection of rotation resistant rope.
(e) Any new poured socket or swaged socket assembly used as a standing rope (guy) shall be proof tested to the side boom tractor or fitting manufacturer's recommendation, but in no case greater than 50% of the component wire rope, structural strand, or fitting(s) nominal strength.
14-2.4.2 Rope Replacement
(a) No precise rules can be given for determination of the exact time for rope replacement, since many variable factors are involved. Once a rope reaches any one of the specified removal criteria, if may be allowed to operate to the end of the work shift, based on the judgment of a qualified person. The rope shall be replaced after a work shift, at the end of the day, or at the latest time prior to the equipment being used by the next work shift.
(b) Removal criteria for rope replacement shall be as follows:
(1) in running ropes, six randomly distributed broken wires in one lay or three broken wires in one stand in one lay
(2) wear of one-third the original diameter of out-side individual wires
(3) kinking, crushing, birdcaging, or any other damage resulting in distortion of the rope structure
(4) evidence of heat damage
(5) reductions from nominal diameter of more than:
(a) 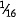 in. (0.4 mm) for diameters up to and including
in. (0.4 mm) for diameters up to and including 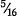 in. (7.9 mm)
in. (7.9 mm)
(b) 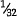 in. (0.8 mm) for diameters ⅜ in. (9.5 mm) up to and including ½ in (13 mm)
in. (0.8 mm) for diameters ⅜ in. (9.5 mm) up to and including ½ in (13 mm)
(c) 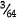 in. (1.2 mm) for diameters
in. (1.2 mm) for diameters 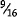 in. (14.3 mm) up to and including ¾ in. (19 mm)
in. (14.3 mm) up to and including ¾ in. (19 mm)
(d) 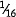 in. (1.6 mm) for diameters ⅞ in. (22 mm) up to and including 1⅛ in. (29 mm)
in. (1.6 mm) for diameters ⅞ in. (22 mm) up to and including 1⅛ in. (29 mm)
(e) 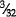 in. (2.4 mm) for diameters 1¼ in. (32 mm) up to and including 1½ in. (38 mm)
in. (2.4 mm) for diameters 1¼ in. (32 mm) up to and including 1½ in. (38 mm)
(6) in standing ropes, more than two broken wires in one lay in sections beyond end connections, or more than one broken wire at an end connection
(c) Broken wire removal criteria cited in this volume apply to wire rope operating on steel sheaves and drums. The user shall contact the sheave, drum, or side boom tractor manufacturer, or a qualified person for broken
11wire removal criteria for wire ropes operating on sheaves and drums made of material other than steel.
(d) In order to establish data as a basis of judging the proper time for replacements, a continuing inspection record should be maintained. This record shall cover points of deterioration listed in para. 14-2.4.1.
(e) Replacement rope shall be the same size, grade, and construction as the original rope furnished by the manufacturer, unless otherwise recommended by a rope manufacturer or a qualified person due to actual working condition requirements.
(f) Discarded rope should not be used for slings.
14-2.4.3 Rope Maintenance
(a) Rope should be stored to prevent damage or deterioration.
(b) Unreeling or uncoiling of rope shall be done as recommended by the rope manufacturer(s) or a qualified person and with care to avoid kinking or inducing a twist.
(c) Before cutting a rope, means shall be used to prevent unlaying of the stands.
(d) During installation, care should be observed to avoid dragging the rope in dirt or around objects that will scrape, nick, crush, or induce sharp bends.
(e) Rope should be maintained in a well-lubricated condition. Lubricant applied as part of a mainteance program shall be compatible with the original lubricant and the rope manufacturer should be consulted. Lubricant applied shall be of the type that does not hinder visual inspection. Those sections of rope that are located over sheaves or otherwise hidden during inspection and maintenance procedures require special attention when lubricating rope. The object of rope lubrication is to reduce internal friction and to prevent corrosion.
1214-3.1.1 Operators
(a) Side boom tractors shall be operated only by the following personnel:
(1) designated persons
(2) trainees under the direct supervision of a designated person
(3) maintenance and test personnel, when it is necessary in the performance of their duties.
(b) No one, other than personnel specified in para. 14-3.1.1(a), shall enter the operator station, with the exception of persons such as maintenance personnel and supervisors, whose duties require them to do so, and then only in the performance of their duties and with the knowledge of the operator or other appointed personnel.
14-3.1.2 Operator Qualifications
(a) When required by law, operators shall be required to pass a practical operating examination. Examinations shall be limited to the specific type equipment that a person will operate.
(b) Operators shall meet the following physical requirements:
(1) vision of at least 20/30 Snellen in one eye, and 20/50 in the other, with or without corrective lenses
(2) ability to distinguish red, green, and yellow, regardless of position of colors, if color differentiation is required for operation.
(3) hearing, with or without hearing aid, must be adequate for the specific operation
(4) history of epilepsy or of a disabling heart condition shall be sufficient reason for the operator's disqualification
14-3.1.3 Operating Practices
(a) The operator shall not engage in any practice that will divert his attention while actually engaged in operating the side boom tractor.
(b) When physically or otherwise unfit, an operator shall not engage in the operation of the equipment.
(c) The operator shall respond to signals only from the appointed signalperson but shall obey a STOP signal at any time, no matter who gives it.
(d) Each operator shall be responsible for those operations under the operator's direct control. Whenever there is any doubt as to safety, the operator shall consult with the supervisor before handling the loads.
(e) If a warning signal is furnished, it shall be sounded each time before traveling, and intermittently during travel, particularly when approaching work-persons.
(f) Before leaving the side boom tractor unattended, the operator shall:
(1) land any attached load, bucket, lifting magnet, or other device, if practical
(2) disengage clutch
(3) set travel brakes, boom brakes, and other clocking devices
(4) put controls in the off position
(5) stop the engine
(6) secure the side boom tractor against inadvertent travel
(7) lower the boom to the ground level or otherwise secure it against displacement by wind loads or other outside forces
(g) If there is a warning sign on the switch or engine starting controls, the operator shall not close the switch or start the engine until it is removed by authority of the person who placed the sign on the machine.
(h) The operator shall verify that all controls are in a position recommended by the manufacturer and all personnel are in the clear before starting the engine.
(i) if power fails during operation, the operator shall:
(1) set all brakes and locking devices
(2) move all clutch or other power controls to the off position
(3) land the suspended load under brake control, if practical
(j) The operator shall be familiar with the equipment and its proper care. If adjustments or repairs are necessary, or any defects are known, the operator shall report the same promptly to the appointed person who shall be responsible for the operation and maintenance repairs of the side boom tractor. The operator shall also notify the next operator of any remaining, uncorrected defects upon changing shifts.
(k) All controls shall be tested by the operator at the start of a new shift. If any controls do not operate properly, they shall be adjusted or repaired before operations are begun.
(l) Booms that are being assembled or disassembled on the ground, with or without support of the boom harness, should be blocked to prevent dropping of the boom and boom sections.
1314-3.2.1 Weight of Load
(a) No side boom tractor shall be loaded beyond the maximum load capacity, except for test purposes as provided in para. 14-2.2
(b) When loads that are limited by structural competence rather than by stability are to be handled, the person responsible for the job shall ascertain that the weight of the load has been determined within ±10% before it is lifted.
(c) When the load lifted results in design factors of less than 4.0 for running ropes or 3.5 for standing ropes, the requirements listed below shall be met:
(1) An inspection prior to and following the lift reveals no deficiencies of the rope, per para. 14-2.4.
(2) The maximum load capacity of the side boom is not exceeded.
(3) The load can be and is handled in such manner and at such speeds as to minimize dynamic effects.
(4) The lift and inspections are made under controlled conditions and under the direction of a qualified person.
14-3.2.2 Attaching the Load
(a) The hoist rope shall not be wrapped around the load.
(b) The load shall be attached to the hook by means of slings or other devices.
14-3.2.3 Moving the Load
(a) The individual directing the lift shall see that the load is secured and balanced in the sling or lifting device before it is lifted more than a few inches.
(b) Before starting to lift, note the following conditions:
(1) Hoist rope shall not be kinked.
(2) Multiple-part lines shall not be twisted around each other.
(3) The hook shall be brought over the load in such a manner as to prevent swinging.
(4) If there is a slack rope condition, it should be determined that the rope is properly seated on the drum and in the sheaves.
(c) During lifting, care should be taken that:
(1) there is no sudden acceleration or deceleration of the moving load.
(2) the load does not contact any obstructions.
(d) Side loading of booms should be limited to freely suspended loads.
(e) The operator shall not lift, lower, or travel while anyone is on the load or hook, except when the hook is attached to landed pipe placed in trench.
(f) The operator should avoid carrying loads over people.
(g) The operator shall test the load and boom brakes each time a load approaching the rated load is handled.
(h) If equipped by the manufacturer, stabilizers shall be used when the load to be handled at that particular load overhang exceeds the rated load without stabilizers, as specified by the manufacturer. Where floats are used, they shall be attached to the stabilizers. Wood blocks used to support stabilizers shall be:
(1) strong enough to prevent crushing, bending, or shear failure
(2) of such thickness, width, and length as to completely support the float, transmit the load to the supporting surface, and prevent shifting, toppling, or excessive settlement under load
(3) used only under the outer bearing surface of the extended stabilizer beam
(i) Neither the load nor the boom shall be lowered below the point where less than two full wraps of rope remain on their respective drums.
(j) When two or more side boom tractors are used to lift one load, one designated person shall be responsible for operation. He shall analyze the operation and instruct all personnel involved in the proper positioning, rigging of the load, and the movements to be made.
(k) In transit, the following additional precaution shall be exercised: the empty hook shall be lashed or otherwise restrained so that it cannot swing freely.
(l) Before traveling a side boom tractor with load, a qualified person shall be responsible for determining and controlling safety. Decisions such as position of load, boom location, ground support, travel route, and speed of movement shall be in accord with that person's determinations.
(m) When a side boom tractor is to be operated at a fixed boom overhang, the bottom hoist pawl or other positive locking device shall be engaged.
14-3.2.4 Holding the Load
(a) The operator shall not leave the controls while the load is suspended.
(b) As an exception to para. 14-3.2.4(a), under such circumstances where a load is to be held suspended for a period of time exceeding normal lifting operations, the operator may leave the controls, provided prior to that time the appointed individual and operator shall establish the requirements for restraining the boom and load.
(c) No person should be permitted to stand or pass under a suspended load.
14-3.3.1 Standard Signals
Standard signals to the operator shall be in accordance with the standards prescribed in para. 14-3.3.2 unless voice communication equipment (telephone, radio, or equivalent) is utilized. Signals shall be discernible or
14audible at all times. No response shall be made unless signals are understood.
14-3.3.2 Hand Signals
Hand Signals shall be in accordance with Fig. 4 and shall be posted conspicuously.
14-3.3.3 Special Signals
For operations not covered by para. 14-3.3.2 or for special conditions that occur from time to time, additions to or modifications of the standard signals may be required. In such cases these special signals shall be agreed on in advance by the operator and the signalperson and should not be in conflict with standard signals.
14-3.3.4 Instructions
If it is desired to give instructions to the operator, other than provided by the established signal system, the side boom tractor motions shall be stopped.
14-3.4.1 Counterweight
Counterweights shall be used in accordance with the manufacturer's specifications.
14-3.4.2 Operating Near Electric Power Lines
(a) Side boom tractors shall be operated so that no part of the side boom tractor or load enters into the Danger Zone shown in Fig. 5.
EXCEPTIONS: The Danger Zone may be entered if
(a) the electrical distribution and transmission lines have been deenergized and visibly grounded at the point of work
(b) insulating barriers (not a part of nor an attachment to the side boom tractor) have been erected to prevent physical contact with the lines
(1) For lines rated 50 kV or below, minimum clearance between the lines and any part of the side boom tractor or load (including handling appendages) shall be 10 ft (3.0 m). For higher voltages, see Table 1.
(2) Caution shall be exercised when working near overhead lines because they can move horizontally or vertically due to wind, moving the danger zone to new positions.
(3) In transit with no load and boom lowered, the clearance shall be as specified in Table 1.
(4) A qualified signalperson shall be assigned to observe the clearance and give warning before approaching the limits specified in Table 1.
(b) Before the commencement of operations near electrical lines, the person responsible for the job shall notify the owners of the lines or their authorized representative, providing them with all pertinent information and requesting their cooperation.
(c) Any overhead wire shall be considered to be an energized line unless and until the person owning such line or the electrical utility authorities verify that it is not an energized line.
(d) Exceptions to this procedure, if approved by the owner of the electrical lines, may be granted by the administrative or regulatory authority if the alternate procedure provides sufficient protection and is set forth in writing.
(e) If cage-type boom guards, insulating links, or proximity warning devices are used on side boom tractors, such devices shall not be a substitute for the requirements of para. 14-3.4.2(a) even if such devices are required by law or regulation. Limitations of such devices shall be understood by operating personnel and tested in the manner prescribed by the manufacturer of the device.
(f) Durable signs shall be installed at the operator's station and on the outside of the side boom tractor, warning that electrocution or serious bodily injury may occur unless a minimum clearance of 10 ft (3.0 m) is maintained between the side boom tractor or the load being handled and energized power lines. Greater clearances are required because of higher voltage as stated in para. 14-3.4.2(a)(1). Signs shall be revised but not removed when local jurisdiction requires greater clearances.
14-3.4.3 Refueling
(a) When refueling with a small portable container, it shall be a safety-type can equipped with automatic closing cap and flame arrester.
(b) Gasoline powered machines shall not be refueled with the engine running.
(c) Smoking or open flames shall be prohibited in the refueling area.
14-3.4.4 Fire Extinguishers
(a) A portable fire extinguisher, with a minimum extinguisher rating of 10 BC, shall be installed in the cab or at the machinery housing.
(b) Operating and maintenance personnel shall be familiar with the use and care of the fire extinguisher provided.
15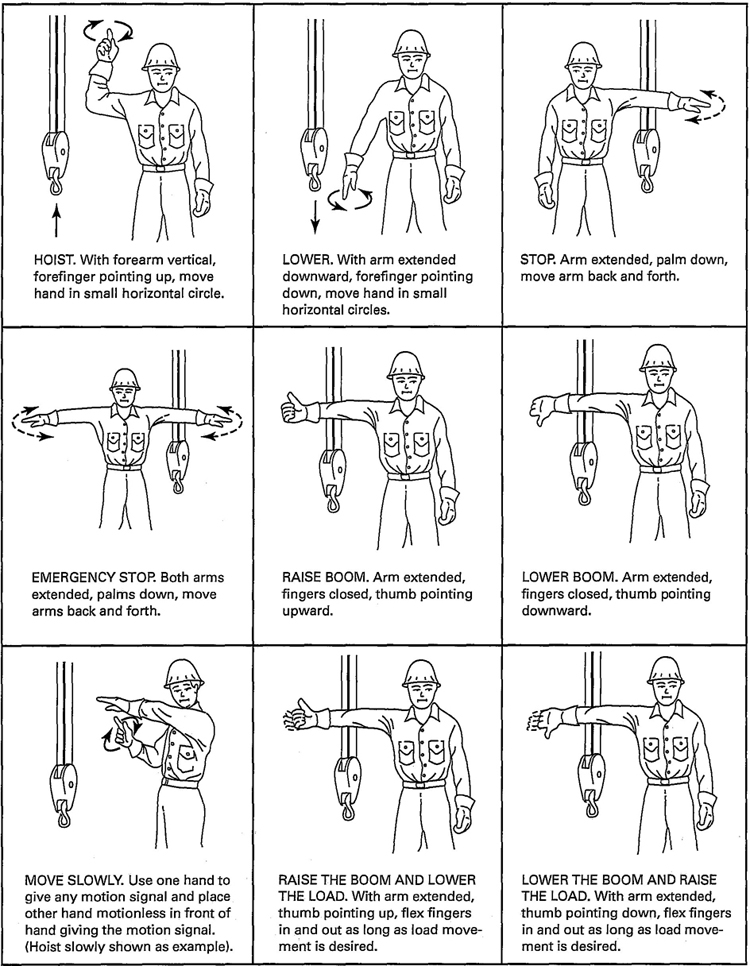
Fig. 4 Standard Hand Signals for Controlling Side Boom Tractor Operations
16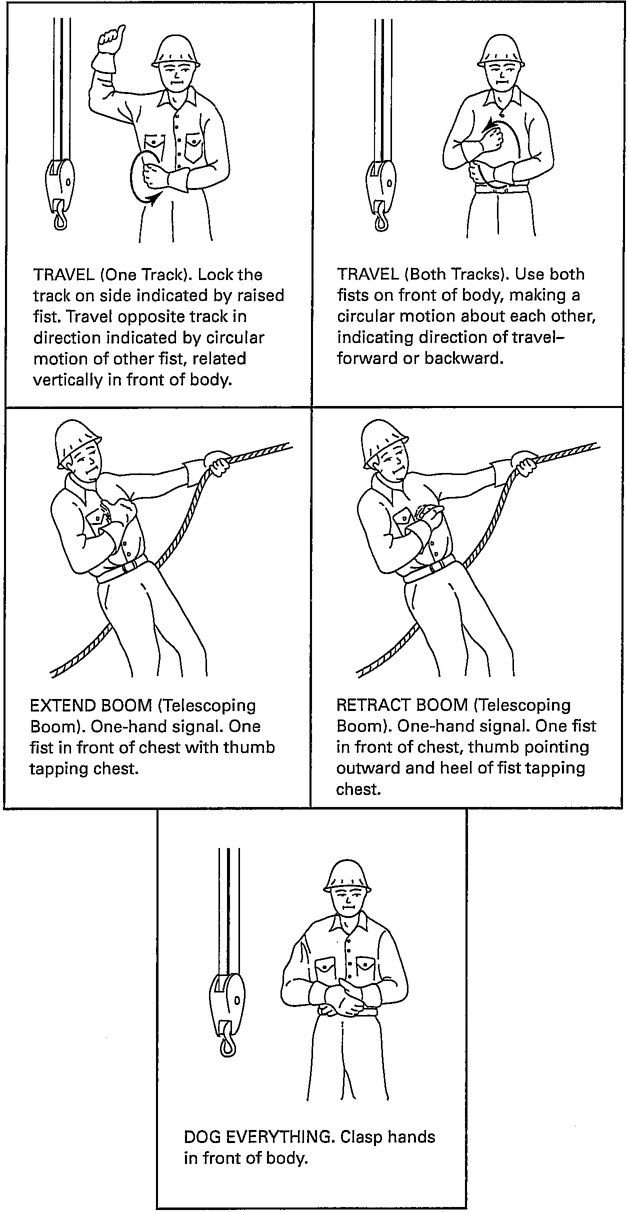
Fig. 4 Standard Hand Signals for Controlling Side Boom Tractor Operations (Cont'd)
17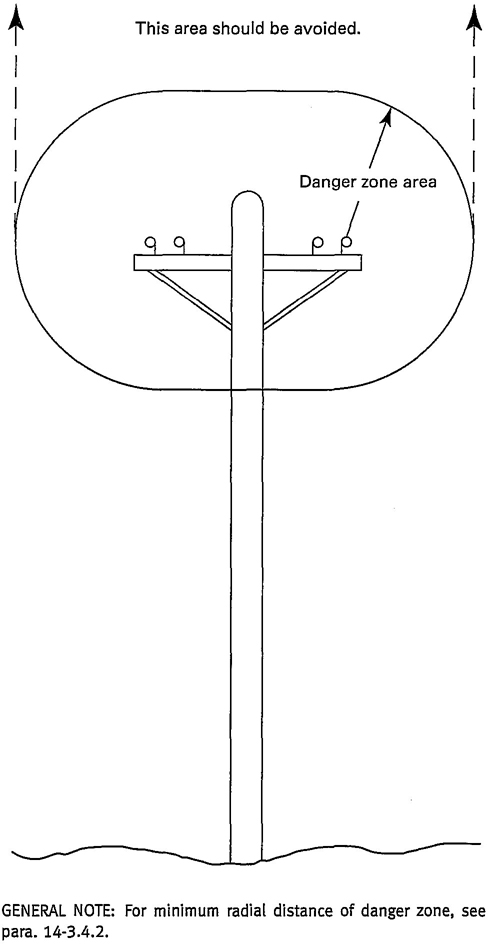
GENERAL NOTE: For minimum radial distance of danger zone, see para. 14-3.4.2
Fig. 5 Danger Zone for Side Boom Tractors and Lifted Loads Operating Near Electrical Transmission Lines
| Normal Voltage, kV (Phase to Phase) |
Minimum Required Clearance | |
|---|---|---|
| ft | (m) | |
| Operation Near High Voltage Power Lines | ||
| To 50 | 10 | (3.05) |
| Over 50 to 200 | 15 | (4.60) |
| Over 200 to 350 | 20 | (6.10) |
| Over 350 to 500 | 25 | (7.62) |
| Over 500 to 750 | 35 | (10.67) |
| Over 750 to 1000 | 42 | (12.80) |
| Operation in Transit With No Load and Boom or Mast Lowered | ||
| To 0.75 | 4 | (1.22) |
| Over 0.75 to 50 | 6 | (1.83) |
| Over 50 to 345 | 10 | (3.05) |
| Over 350 to 750 | 16 | (4.87) |
| Over 750 to 1000 | 20 | (6.10) |
ASME B30.14-2004
