
In order to promote public education and public safety, equal justice for all, a better informed citizenry, the rule of law, world trade and world peace, this legal document is hereby made available on a noncommercial basis, as it is the right of all humans to know and speak the laws that govern them.

EAS 128:2011
ICS 67.060.10
EAST AFRICAN COMMUNITY
HS 1006.30.00
© EAC 2011
Second Edition 2011
iDevelopment of the East African Standards has been necessitated by the need for harmonizing requirements governing quality of products and services in East Africa. It is envisaged that through harmonized standardization, trade barriers which are encountered when goods and services are exchanged within the Community will be removed.
In order to meet the above objectives, the EAC Partner States have enacted an East African Standardization, Quality Assurance, Metrology and Test Act, 2006 (EAC SQMT Act, 2006) to make provisions for ensuring standardization, quality assurance, metrology and testing of products produced or originating in a third country and traded in the Community in order to facilitate industrial development and trade as well as helping to protect the health and safety of society and the environment in the Community.
East African Standards are formulated in accordance with the procedures established by the East African Standards Committee. The East African Standards Committee is established under the provisions of Article 4 of the EAC SQMT Act, 2006. The Committee is composed of representatives of the National Standards Bodies in Partner States, together with the representatives from the private sectors and consumer organizations. Draft East African Standards are circulated to stakeholders through the National Standards Bodies in the Partner States. The comments received are discussed and incorporated before finalization of standards, in accordance with the procedures of the Community.
Article 15(1) of the EAC SQMT Act, 2006 provides that “Within six months of the declaration of an East African Standard, the Partner States shall adopt, without deviation from the approved text of the standard, the East African Standard as a national standard and withdraw any existing national standard with similar scope and purpose”.
East African Standards are subject to review, to keep pace with technological advances. Users of the East African Standards are therefore expected to ensure that they always have the latest versions of the standards they are implementing.
© East African Community 2011 — All rights reserved*
East African Community
P O Box 1096
Arusha
Tanzania
Tel: 255 27 2504253/8
Fax: 255-27-2504481/2504255
E-Mail: eac@eachq.org
Web: www.each.int
* © 2011 EAC — All rights of exploitation in any form and by any means reserved worldwide for EAC Partner States’ NSBs.
iiThis standard has been developed to take into account:
| 1 | Scope | 1 | ||
| 2 | Normative references | 1 | ||
| 3 | Terms and Definitions | 1 | ||
| 4 | Quality requirements | 6 | ||
| 4.2 | General requirements | 6 | ||
| 4.3 | Specific requirements | 6 | ||
| 4.3.1 | Grading | 6 | ||
| 4.3.2 | Ungraded milled rice | 7 | ||
| 4.4 | Reject grade milled rice | 7 | ||
| 5 | Contaminants | 7 | ||
| 5.1 | Heavy metals | 7 | ||
| 5.2 | Pesticide residues | 8 | ||
| 5.3 | Mycotoxin limits | 8 | ||
| 6 | Hygiene | 8 | ||
| 7 | Packaging | 8 | ||
| 8 | Labelling | 9 | ||
| 9 | Sampling methods | 9 | ||
Milled rice — Specification
This East African Standard specifies the requirements and methods of sampling and test for milled rice of the varieties grown from Oryza spp. intended for human consumption..
The following normative documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text constitute provisions of this East African Standards
ISO 605, Pulses — Determination of impurities, size, foreign odours, insects, and species and variety — Test methods
ISO 711, Cereals and cereal products — Determination of moisture content (Basic reference method)
ISO 712, Cereals and cereal products — Determination of moisture content — Routine reference method
ISO 5223, Test sieves for cereals
ISO 6639-1, Cereals and pulses — Determination of hidden insect infestation — Part 1: General principles
ISO 6639-2, Cereals and pulses — Determination of hidden insect infestation — Part 2: Sampling
ISO 6639-3, Cereals and pulses — Determination of hidden insect infestation — Part 3: Reference method
ISO 6639-4, Cereals and pulses — Determination of hidden insect infestation — Part 4: Rapid methods
ISO 13690, Cereals, pulses and milled products — Sampling of static batches
ISO 16050, Foodstuffs — Determination of aflatoxin B1, and the total content of aflatoxin B1, B2, G1 and G2 in cereals, nuts and derived products — High performance liquid chromatographic method
EAS 38, Labelling of prepackaged foods — Specification
EAS 79, Cereals and pulses as grain — Methods of sampling
EAS 217, Methods for the microbiological examination of foods
EAS 39, Hygiene in the food and drink manufacturing industry — Code of practice
CODEX Stan 193, Codex general Standards for contaminants and toxins in Food and Feed
For the purpose of this East African Standard, the following definitions shall apply.
whole or broken kernels of rice (Oryza spp from which the hulls and at least the outer bran layers have been removed.
1a by product from milling consisting of the outer (pericarp) layers of the kernel with part of the germ
special varieties of rice (Oryza sativa L. scented) that have a distinctive and characteristic aroma; e.g., basmati and jasmine rice
pieces of rice that are less than three-quarters of a whole kernel and includes grains of rice in which part of the endosperm is exposed or rice without a germ. If the piece is more than three-quarters of a kernel, it is considered whole.
hole or broken kernels of rice from which the hulls have been removed
head rice or broken kernel of non-parboiled rice, except wax rice, whose whole surface has an opaque and floury appearance
part of kernel which passes through a metal sieve with round perforations 1.4 mm in diameter
There are four classes of milled rice. The following four classes shall be based on the percentage of whole kernels, and types of rice:
Long Grain Milled Rice.
Medium Grain Milled Rice.
Short Grain Milled Rice.
Mixed Milled Rice.
kernels, pieces of rice kernels, and other grains that are badly ground-damaged, badly weather-damaged, diseased, frost-damaged, germ-damaged, heat-damaged, injured-by-heat, insect-bored, field fungi, skinned, mould-damaged, shot or sprout-damaged, dark tipped, pink-stained, over-dried damaged, bin burnt, storage mould affected or rotted, smut, stained or otherwise materially damaged.
2rice obtained by milling husked rice in such a way that all of the bran and almost all of the embryo have been removed
all organic and inorganic material other than pearl millet, broken kernels, other grains and filth.
special varieties of rice (Oryza sativa L. glutinosa) which contain more than 50 percent chalky kernels and have a white and opaque appearance. For long grain, medium grain, and short grain milled rice, Grade 1 shall contain not more than 1.0 percent of nonchalky kernels, Grade 2 not more than 2.0 percent of nonchalky kernels, Grade 3 not more than 4.0 percent of nonchalky kernels, Grade 4 not more than 6.0 percent of nonchalky kernels. For second head milled rice, Grade 1 shall contain not more than 4.0 percent of nonchalky kernels, Grade 2 not more than 6.0 percent of nonchalky kernels, Grade 3 not more than 10.0 percent of nonchalky kernels and Grade 4 not more than 15.0 percent of nonchalky kernels. For screenings milled rice, there are no grade limits for percent of nonchalky kernels. For brewers milled rice, the special category “Glutinous milled rice” is not applicable.
granulated brewers milled rice shall be milled rice which has been crushed or granulated so that 95.0 percent or more will pass through a 5 sieve, 70.0 percent or more will pass through a 4 sieve, and not more than 15.0 percent will pass through a 2 ½ sieve.
whole kernel or part of the kernel with a length greater than or equal to 75 % of the average length of the test sample kernels (see Figure 1)
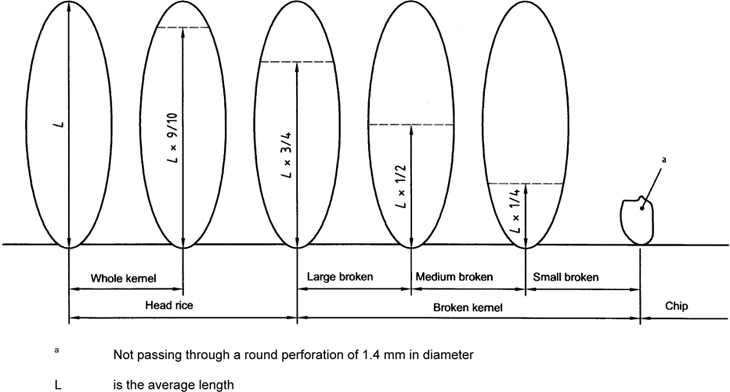
Figure 1 — Size of kernels, broken kernels and chips
whole or broken kernels of rice which are materially discoloured and damaged as a result of heating and parboiled kernels in nonparboiled rice which are as dark as, or darker in color than, the interpretive line for heat-damaged kernels.
3NOTE This category includes the kernel that is yellow/dark yellow in the case of non-parboiled rice and orange/dark orange in the case of parboiled rice, due to a microbiological alteration.
head rice or broken kernel which is unripe and/or badly developed
grains eaten in part by stored grain insects and any field pests of grains including Heliothis spp. Grains may have a hole (commonly referred to as bored) or have a chewed appearance on any part of the grain.
part of kernel with a length less than three-quarters but greater than one half of the average length of the test sample kernels
part of kernel with a length less than or equal to one half but greater than one quarter of the average length of the test sample kernels (Figure 1)
whole or broken unhulled kernels of rice; whole or broken kernels of brown rice, and whole or broken kernels of milled rice having a portion or portions of the hull remaining which cover 12.5 % or more of the whole or broken kernel
milled rice in which the starch has been gelatinized by soaking, steaming, and drying. Grades 1 to 4, inclusive, shall contain not more than 10.0 percent of ungelatinized kernels. Grades 1 and 2 shall contain not more than 0.1 percent, Grades 3 and 4 not more than 0.2 percent of non parboiled rice. If the rice is:
The colour levels for “Parboiled Light,” “Parboiled,” and “Parboiled Dark” shall be in accordance with the interpretive line samples for parboiled rice.
NOTE The maximum limits for “Chalky kernels,” “Heat-damaged kernels,” “Kernels damaged by heat”, and the “Colour requirements” are not applicable to the special grade “Parboiled milled rice.”
head rice or kernel of parboiled rice which is not fully gelatinized and shows a distinct white opaque area
head rice or broken kernel of parboiled rice of which more than 25 % of the surface is dark brown or black in colour due to the parboiling process
4any seed which if present in quantities above permissible limit may have damaging or dangerous effect on health, organoleptic properties or technological performance such as Jimson weed — dhatura (D. fastuosa Linn and D. stramonium Linn.) corn cokle (Agrostemma githago L., Machai Lallium remulenum Linn.) Akra (Vicia species), Argemone mexicana, Khesari and other seeds that are commonly recognized as harmful to health
head rice or broken kernel having a red bran covering more than 25 % of its surface
head rice or broken kernel with red bran streaks of length greater than or equal to 50 % of that whole kernel, but where the surface covered by these red streaks is less than 25 % of the total surace
kernels that are discoloured, swollen and soft as a result of decomposition by fungi or bacteria. They may feel spongy under pressure. There is a single tolerance for the total of binburnt, severely mildewed, mouldy, and rotten kernels.
milled rice which is not equal to the milling requirements for “well milled,” and “reasonably well milled” rice. Grades 1 and 2 shall contain not more than 2.0 percent, Grades 3 and 4 not more than 5.0 percent of well-milled kernels.
whole or broken kernels of parboiled rice with distinct white or chalky areas due to incomplete gelatinization of the starch
whole or broken kernels of rice from which the hulls and practically all of the germs and the bran layers have been removed
NOTE this factor is determined on an individual kernel basis and applies to the special grade Under-milled milled rice only.
unbroken kernels of rice and broken kernels of rice which are at least three-fourths of an unbroken kernel
The rough or brown rice from which the milled rice is obtained shall be of sound quality, free from sand, have characteristic odour and flavour complying with the relevant East African Standards
Milled rice shall meet the following general requirements/limits as determined using the relevant standards listed in Clause 2:
Milled rice grains for human consumption shall be graded into three grades on the basis of the tolerable limits established in Table 1 which shall be additional to the general requirements set out in this standard.
6Shall be milled rice which does not fall within the requirements of Grades 1, 2, and 3 of this standard but is not rejected rice grains.
Note: For Tanzania and Burundi this requirement shall not apply.
This comprises milled rice which has objectionable odour, off flavour, living insects or which do not possess the quality characteristics specified in Table 1. It cannot satisfy the conditions of ungraded milled rice and shall be graded as reject milled rice and shall be regarded as unfit for human consumption.
| Characteristics | Maximum limits | Test Method | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 3 | ||
| Broken, % | 5 | 7 | 15 | ISO 605 |
| Heat damaged rice, % | 1 | 1.5 | 2.0 | |
| Damaged rice, % | 1.5 | 2 | 3.0 | |
| Chalkya % | 2 | 4 | 10 | |
| Red or red streaked, % | 2 | 6 | 12 | |
| immature grains, % | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | |
| Other contrasting varieties, % | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Organic matter, % | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.5 | |
| Inorganic matter, % | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | |
| Paddy grains, % | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| Live weevils/kg | Nil | Nil | Nil | |
| Filth, % | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | |
| Moisture contents, % | 13 | 13 | 13 | EAS 82/ISO 712 |
| Total Aflatoxin (AFB1+AFB2+AFG1 +AFG2)), ppb | 10 | ISO 16050 | ||
| Aflatoxin B1 only, ppb | 5 | |||
| Fumonisin ppm | 2 | |||
Milled rice shall comply with those maximum limits for heavy metals established by the Codex Alimentarius Commission for this commodity.
7Milled rice shall comply with those maximum pesticide residue limits established by the Codex Alimentarius Commission for this commodity
Note: where the use of certain pesticides is prohibited by some Partner States, then it shall be notified to all Partner States accordingly.
Milled rice shall comply with those maximum mycotoxin limits established by the Codex Alimentarius Commission for this commodity. In particular, total aflatoxin levels in milled rice for human consumption shall not exceed 10 µg/kg (ppb) with B1 not exceeding 5 µg/kg (ppb) when tested according to ISO 16050.
Milled rice shall be produced, prepared and handled in accordance with the provisions of appropriate sections of EAS 39
When tested by appropriate standards of sampling and examination listed in Clause 2, the products:
| Type of micro-organism | Limits | Test method | |
|---|---|---|---|
| i) | Yeasts and moulds, max. per g | 102 | EAS 217 |
| ii) | S. aureus per 25 g | Not detectable | |
| iii) | E. Coli, max. per g | Not detectable | |
| iv) | Salmonella, max. per 25 g | Not detectable |
Milled rice shall be packed in suitable packages which shall be clean, sound, free from insect, fungal infestation and the packing material shall be of food grade quality.
Milled rice shall be packed in containers which will safeguard the hygienic, nutritional, technological and organoleptic qualities of the products.
The containers, including packaging material, shall be made of substances which are safe and suitable for their intended use. They shall not impart any toxic substance or undesirable odour or flavour to the product.
Each package shall contain rice of the same type and of the same grade designation.
If milled rice is presented in bags, the bags shall also be free of pests and contaminants.
8Each package shall be securely closed and sealed.
In addition to the requirements in EAS 38, each package shall be legibly and indelibly marked with the following:
Note: EAC partner states are signatory to the International Labour Organizations (ILO) for maximum package weight of 50kg where human loading and offloading is involved
Sampling shall be done in accordance with the EAS 79/ISO 13690.
9 10